This is a post of the work done at BloomReach on smarter index & data management in SolrCloud.
Authors: Nitin Sharma – Search Platform Engineer & Suruchi Shah – Engineering Intern
Introduction
In a multi-tenant search architecture, as the size of data grows, the manual management of collections, ranking/search configurations becomes non-trivial and cumbersome. This blog describes an innovative approach we implemented at BloomReach that helps with an effective index and a dynamic config management system for massive multi-tenant search infrastructure in SolrCloud.
Problem
The inability to have granular control over index and config management for Solr collections introduces complexities in geographically spanned, massive multi-tenant architectures. Some common scenarios, involving adding and removing nodes, growing collections and their configs, make cluster management a significant challenge. Currently, Solr doesn’t offer a scaling framework to enable any of these operations. Although there are some basic Solr APIs to do trivial core manipulation, they don’t satisfy the scaling requirements at BloomReach.
Innovative Data Management in SolrCloud
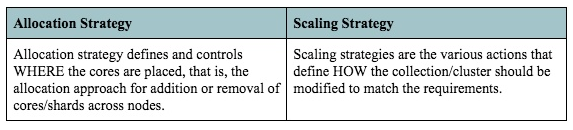
To address the scaling and index management issues, we have designed and implemented the Rebalance API, as shown in Figure 1. This API allows robust index and config manipulation in SolrCloud, while guaranteeing zero downtime using various scaling and allocation strategies. It has two dimensions:
The seven scaling strategies are as follows:
- Auto Shard allows re-sharding an entire collection to any number of destination shards. The process includes re-distributing the index and configs consistently across the new shards, while avoiding any heavy re-indexing processes. It also offers the following flavors:
- Flip Alias Flag controls whether or not the alias name of a collection (if it already had an alias) should automatically switch to the new collection.
- Size-based sharding allows the user to specify the desired size of the destination shards for the collection. As a result, the system defines the final number of shards depending on the total index size.
- Redistribute enables distribution of cores/replicas across unused nodes. Oftentimes, the cores are concentrated within a few nodes. Redistribute allows load sharing by balancing the replicas across all nodes.
- Replace allows migrating all the cores from a source node to a destination node. It is useful in cases requiring replacement of an entire node.
- Scale Up adds new replicas for a shard. The default allocation strategy for scaling up is unused nodes. Scale up also has the ability to replicate additional custom per-merchant configs in addition to the index replication (as an extension to the existing replication handler, which only syncs the index files)
- Scale Down removes the given number of replicas from a shard.
- Remove Dead Nodes is an extension of Scale Down, which allows removal of the replicas/shards from dead nodes for a given collection. In the process, the logic unregisters the replicas from Zookeeper. This in-turn saves a lot of back-and-forth communication between Solr and Zookeeper in their constant attempt to find the replicas on dead nodes.
- Discovery-based Redistribution allows distribution of all collections as new nodes are introduced into a cluster. Currently, when a node is added to a cluster, no operations take place by default. With redistribution, we introduce the ability to rearrange the existing collections across all the nodes evenly.